Heart Health Conditions & Information | Walgreens
Healthy living
starts at the heart
Feel empowered to take control of your heart health. Find helpful services, expert information, recipes, workouts, supplements and products.


Heart health answers
From spotting heart disease-related symptoms to managing your diagnosis, we’re here to help.
- What is heart disease?Heart disease is a general term used to describe conditions that affect the heart or blood vessels. There are many different forms of heart disease, however, coronary artery disease is the most common form of heart disease in the United States.
- What are the symptoms of heart disease?Angina is a common symptom of coronary artery disease. It may feel like pain, pressure or a squeezing sensation in your chest, shoulders, arms, neck, jaw or back. Angina can feel like indigestion, and it tends to feel worse when you are physically active or under emotional stress. Shortness of breath is another common symptom of the condition. However, coronary heart disease doesn’t always cause symptoms. In silent coronary heart disease, the first signs of heart disease are symptoms of a heart attack, heart failure or arrhythmia.
- What are some of the common treatments for heart disease?You can control heart disease and reduce your risk of heart attack with lifestyle changes, such as diet, exercise, healthy weight management, quitting smoking, and taking care of your teeth, and possibly medications. In some cases, your cardiologist may recommend a surgery or procedure to improve blood flow to the heart.
- What is coronary artery disease?Coronary heart disease involves narrowing and hardening of the arteries that supply the heart. This makes it more difficult for blood to flow through the arteries. If a blood clot forms in the arteries that supply the heart or brain, it can block the flow of blood, and a heart attack or stroke can occur.
- What is a heart attack?A heart attack occurs when blood flow to the heart is blocked by a blood clot. This can cause damage or death to part of the heart muscle.
- What is congestive heart failure?Heart failure happens when your heart doesn’t pump blood as well as it should. This means your body doesn’t receive enough blood and oxygen.
- What is arrythmia?Arrhythmia is an abnormal heart rate or rhythm. The heart can beat too fast, too slow or irregularly. There are several types of arrhythmia, and each kind can produce a range and variety of symptoms. Some people experience the condition as a single skipped heartbeat while others feel a fluttering or quivering sensation in their hearts. Over time, arrhythmias can affect how well your heart works.
How do you prevent heart disease?

Diet

Exercise
Stop smoking

Limit alcohol

Reduce stress

Quality sleep
Healthy weight
Helpful resources

Heart disease risk factors
Download ›
Heart healthy tips
Download ›
Related articles

Taking the pressure off hypertension
Living with high blood pressure? Get thoughtful, individualized care at your local Walgreens.
- What is hypertension?Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, occurs when the blood pushing against blood vessel walls generates a force that is considered higher than normal. Overtime, the heart must work harder to pump blood through the blood vessels.
- What causes hypertension?For most adults, there is no identifiable cause of high blood pressure. This type of hypertension is called primary (essential) hypertension and tends to develop gradually over time as you get older. However, secondary hypertension is caused by an underlying health condition or medication. This type of hypertension tends to appear suddenly and causes higher blood pressure levels than primary hypertension.
- What are the symptoms of hypertension?Hypertension often presents no symptoms but increases the risk for heart disease, stroke or other serious health conditions. Severe or long-standing hypertension that is untreated may cause symptoms such as headache, confusion, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, shortness of breath, restlessness, chest pain or abdominal pain that may be a sign of other emergent complications. The only way to know if you have hypertension is to get your blood pressure checked regularly by your healthcare provider.
- How is hypertension prevented and managed?Common ways to prevent and manage hypertension include:
- Knowing your blood pressure numbers
- Keeping your weight at a healthy level & exercise
- Maintaining a heart-healthy diet
- Taking your medicine as prescribed, if applicable
- Managing your stress
- Quitting smoking
- Limiting alcohol intake
- When is hypertension a medical emergency?Call 911 and seek immediate emergency care if your blood pressure reading is 180/120 or higher AND you have any of the following symptoms, which may be signs of target organ damage:
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Numbness or weakness
- Change in vision
- Difficulty speaking
- Severe headache
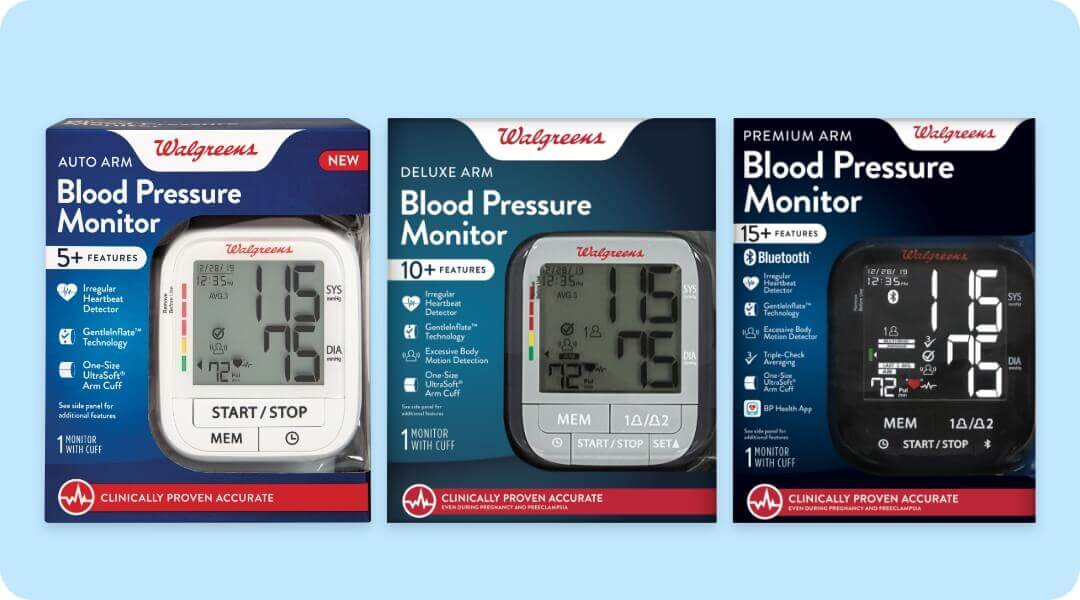
What are the blood pressure readings ranges?
Reference the blood pressure readings ranges below to see what your results may mean:
| Blood Pressure Category | Systolic mm Hg (upper number) | Diastolic mm Hg (lower number) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | Less than 120 | and | Less than 80 |
| Elevated | 120-129 | and | Less than 80 |
| High blood pressure (hypertension) stage 1 | 130-139 | or | 80-89 |
| High blood pressure (hypertension) stage 2 | 140 or higher | or | 90 or higher |
| Hypertensive crisis (consult your doctor immediately) | Higher than 180 | and/or | Higher than 120 |
A diagnosis of high blood pressure must be confirmed with a healthcare provider.
What are the risks associated with
untreated hypertension?
Untreated hypertension may lead to serious health problems including:

Stroke

Heart attack
Peripheral vascular disease
Kidney disease/failure

Complications during pregnancy
Eye damage

Vascular dementia
Helpful resources

Knowing your blood pressure readings
Download ›
What is hypertension?
Download ›

Controlling your blood pressure with healthy habits
Download ›
Supplements & remedies that may lower your blood pressure
Download ›

Checking in on cholesterol
Our pharmacists are trained to provide recommendations around lipid management. We’re here to help you manage your cholesterol.
- What is cholesterol?Cholesterol is a waxy substance made by the liver that is naturally present in the human body. It has many essential functions when it comes to our ability to digest fatty foods and make hormones. Alternately, cholesterol can also be consumed by eating animal-based foods such as meat, poultry and dairy products. While the body does need some cholesterol to work properly too much cholesterol in your blood can increase your risk of coronary artery disease.
- What is total cholesterol, LDL, HDL, and non-HDL?Total cholesterol is a measure of the total amount of cholesterol in your blood. It includes the two main types of cholesterol: low-density lipoproteins (LDL) or “bad” cholesterol, and high-density lipoproteins (HDL) or “good” cholesterol. At normal levels, cholesterol does not pose any threats to overall health. High levels of LDL cholesterol or low levels of HDL cholesterol can raise your risk for heart disease and stroke. Non-HDL is your total cholesterol minus your HDL. Your non-HDL includes LDL and other types of cholesterol.
- What are symptoms of high cholesterol?Usually, high cholesterol has no signs or symptoms. The only way to detect if you have it is through routine blood test. Very high levels of LDL cholesterol may cause symptoms such as grayish-white rings around the corneas of the eye, called corneal arcus, or fatty bumps on your skin, called xanthomas.
- How often should cholesterol be checked?A person’s first cholesterol screening should occur between the ages of 9 and 11, and then be repeated every five years after that. Men ages 45-65 and women ages 55-65 should be screened every one to two years. People over 65 years of age should receive cholesterol tests annually. If your results aren’t within desirable ranges or you have a family history of high cholesterol, heart disease or other risk factors, your doctor may recommend more frequent screenings.
What are considered normal levels of cholesterol?
Normal levels of cholesterol differ depending on your age and sex. The guidelines below show desirable total, non-HDL, LDL and HDL cholesterol levels by age and sex.
| Age and sex | Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | Non-HDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | LDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | HDL cholesterol (mg/dL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| People aged 19 years and younger | Less than 120 | Less than 120 | Less than 110 | More than 45 |
| Men aged 20 years and older | 125-200 | Less than 130 | Less than 100 | 40 or higher |
| Women aged 20 years and older | 125-200 | Less than 130 | Less than 100 | 50 or higher |
What are ways to lower your cholesterol?

Diet

Exercise

Healthy weight

Stop smoking

Medication
Related articles
Helpful resources

How to lower cholesterol naturally
Download ›
What is cholesterol?
Download ›